Table of Contents
1. Overview
2. Parameters apply to GHG Calculations
1. Overview
Greenhouse gas emissions are calculated in FEM based on the energy use values entered inthe Energy section, as well as the refrigerant use listed in the Air section. Emissions are calculated using the 100-year Global Warming Potential factors for each GHG in the IPCC 5th assessment report, including non-carbon GHGs.Energy use values are converted to MJ using the Higher Heating Value (HHV) for each liquid and solid fuel source, where applicable. The literature sources for emission factors are listed below:
| Emission Source | Source |
| Stationary energy sources | EPA 2018 |
| Purchased Electricity | GaBi 2020; IEA 2016 |
| Refrigerants | IPCC 5AR |
2. Parameters apply to GHG Calculations
- All greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulphurhexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) are counted in the GHG inventory. Some individual country-level electricity emission factors may not include some non-carbon emissions due to limited data availability.
- Greenhouse gas emissions are calculated in FEM based on the energy use values entered in the Energy section, as well as the refrigerant use listed in the Air section.
- The calculations are done in accordance with the GHG Protocol, and guidance and training is provided to facilities completing the FEM to ensure compliance with the requirements of the GHG Protocol.
- Emissions are calculated using the 100-year Global Warming Potential (GWP) factors for each GHG in the IPCC 5th assessment report, including non-carbon GHGs.
- Energy use values are converted to MJ using the Higher Heating Value (HHV) for each liquid and solid fuel source, where applicable.
- GHG Calculation Formula: Emission source * conversion to MJ (if applicable) * Emission factor per MJ
- Example: 54 kg (Coal- SBA) *20.077 MJ/kg * 0.09004=92.62 kg GHG
3. Notes for using the GHG calculations
- The emissions reported are based on the total annual energy use and refrigerant emissions for each facility. In order to accurately calculate the emissions associated with a single brand or retailer, the emissions must be allocated using an annual production volume or other metric to properly assign the emissions that brand or retailer is responsible for. Higg provides the “emissions per unit” calculations as one possible option for calculating the properly allocated.
- Electricity emissions are calculated by default on using a location-based, country-level methodology. Users also have the option of using a market-based methodology. Note that contractual instruments used to purchase renewable energy or offsets are not verified by Higg or Cascale.
- Non-renewable and renewable emissions are reported separately. Renewable emissions are only reported at the individual source level, and are not include in any sub-totals or total calculations
- Only energy use and refrigerant use emissions are calculated. No other direct or indirect GHG source emissions are calculated.
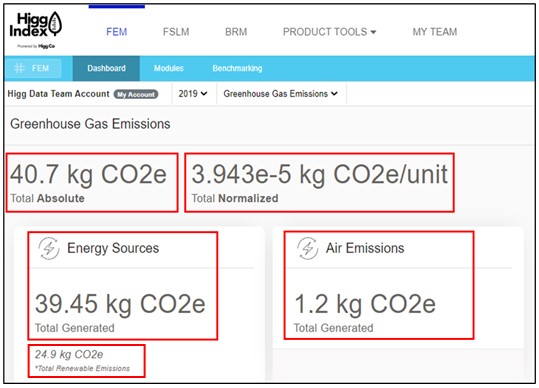
- Total Absolute: Total amount of non-renewable GHG emissions from reporting year (Total Non-renewable Energy Emissions + Total Air Emissions).
- The example screenshot shows: the total absolute amount is 40.7kg CO2e (39.45 + 1.2).
- Total Normalized: Total Emissions per unit of production. The unit of production is based on the unit selected by the facility in the production volume section of Site Info (Total Absolute/Total annual production volume for reported unit).
- The example screenshot shows: the total normalized amount is 3.943e-5 kg CO2e/unit.
- The example screenshot shows: the total normalized amount is 3.943e-5 kg CO2e/unit.
- Energy sources:
- Total Generated: Total amount of non-renewable energy emissions (sum of emissions from each non-renewable source)
- The example screenshot shows: the total amount of non-renewable energy emissions is 39.45kg CO2e.
- The example screenshot shows: the total amount of non-renewable energy emissions is 39.45kg CO2e.
- Total Generated: Total amount of non-renewable energy emissions (sum of emissions from each non-renewable source)
- Total Renewable Emissions: Total amount of renewable (biomass) emissions (sum of emissions from each renewable source)
- The example screenshot shows: the total amount of renewable energy emissions is 24.9kg CO2e.
- The example screenshot shows: the total amount of renewable energy emissions is 24.9kg CO2e.
- Air Emissions:
- Total Generated: total amount of air emissions (refrigerants) (sum of emissions from each refrigerant source).
- The example screenshot shows: the total amount of air emissions is 1.2 kg CO2e.
- Total Generated: total amount of air emissions (refrigerants) (sum of emissions from each refrigerant source).
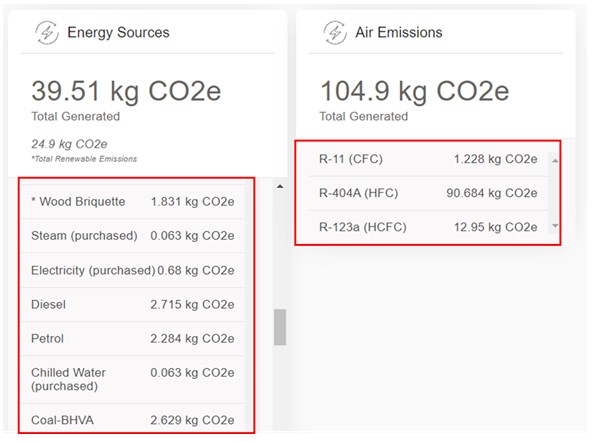
- Individual energy source emissions: emissions for each energy source are listed in this panel. Renewable emissions are listed with an asterisk (*). Note that some renewable sources are zero-emissions, such as solar. Although these sources are considered zero-emission during energy production, there are emissions associated with the manufacturing, installation, and maintenance of these energy sources that are not included in Higg GHG calculations.
- Air Emissions: emissions for each refrigerant emissions source are listed in this panel. Note that not all refrigerants have GWP factors and would show as 0 emissions regardless of the amount entered.
In the FEM CSV bulk export files, you can review the GHG revision data. Below is the updated bulk CSV V2 reference guidance.
