Higg MSI Content Guidance
Universal Material Customization Features
2. Chemistry Management Qualifiers
4. Yield and Unit of Measure Conversions
Material Categories
6. Foam
8. Leather
9. Metals
10. Plastics
13. Textiles
Customizing Trims and Packaging
Content Guidance Overview
Materials in the Higg MSI are organized in a hierarchical manner that allows for use and customization based on the amount of information that is available and can be validated. The general structure is illustrated in the following diagram.
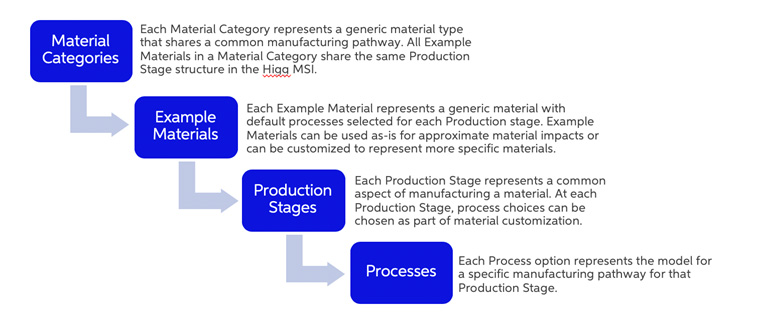
Example:
Textiles is a Material Category
Cotton Fabric is an Example Material within the Textiles Material Category
Raw Material Source is a Production Stage common to all Textiles and therefore used in Cotton Fabric
Cotton fiber, conventional production is a process option within the Raw Material Source Production Stage for Cotton Fabric
The content guidance for the Higg MSI is organized in a similar manner. Choosing a link to a Material Category will provide guidance on selecting the right Example Material from the available options. Further links are organized around Production Stages, with guidance on process selection ranging from broadly applicable to material-specific choices.
Example:
- The current page provides guidance on Material Categories.
- Clicking on “Textiles” in the sidebar takes you to a page that explains the different Example Material options available within Textiles.
- Clicking on a Production Stage, such as Raw Material Source, takes you to a page with specific guidance around selecting processes for that Production Stage.
- The Raw Material Source Production Stage page in the“Cotton Fabric” section shows the different process options and when each one should be chosen.
This page also has links to guidance on the following material customization features that have a common ruleset for all materials in the Higg MSI:
- Chemistry Management Qualifiers
- Transportation Distances
- Yield and Unit of Measure Conversions
- Using and Customizing Trims and Packaging
Materials in the Higg MSI are divided into ten Material Categories:
| Textiles | Flexible materials made from natural and synthetic fibers through weaving, knitting, or non-woven processing. |
| Synthetic Leather | Artificial leather that is made of polymeric materials. |
| Leather | Material made from the skin of an animal by tanning. |
| Leather Alternatives | Plant-based materials, recycled, and other materials that are intended as leather replacements. |
| Plastics | Long-chain polymeric materials that have the capability to be molded and shaped. Most plastics are synthetic but plastics from natural origin are also included. |
| Rubbers/Elastomers | Elastic polymeric materials that can stretch and recover their original shape. Rubbers can be of synthetic or natural origin. |
| Metals | Solid malleable and ductile materials that have high thermal and electrical conductivity. |
| Wood-based Materials | Materials that are prepared directly from trees without chemical processing, as well as paper and cardboard products. |
| Insulation Material | Fiber-based materials that are designed to provide thermal resistance. This includes natural insulations like down as well as synthetic insulations. |
| Coatings and Laminations | Films, membranes, and coatings that are used separately or as a layer in a multi-component material. |
| Foam | Materials that have been expanded to have foam cells by using chemical and/or physical blowing agents. |
